
They both are the two types of spatial data in GIS. Whereas, the raster data represents a grid matrix. The vector data represents data using sequential points or vertices as points, lines and polygons. Hence, there are some primary difference between Vector and Raster data.
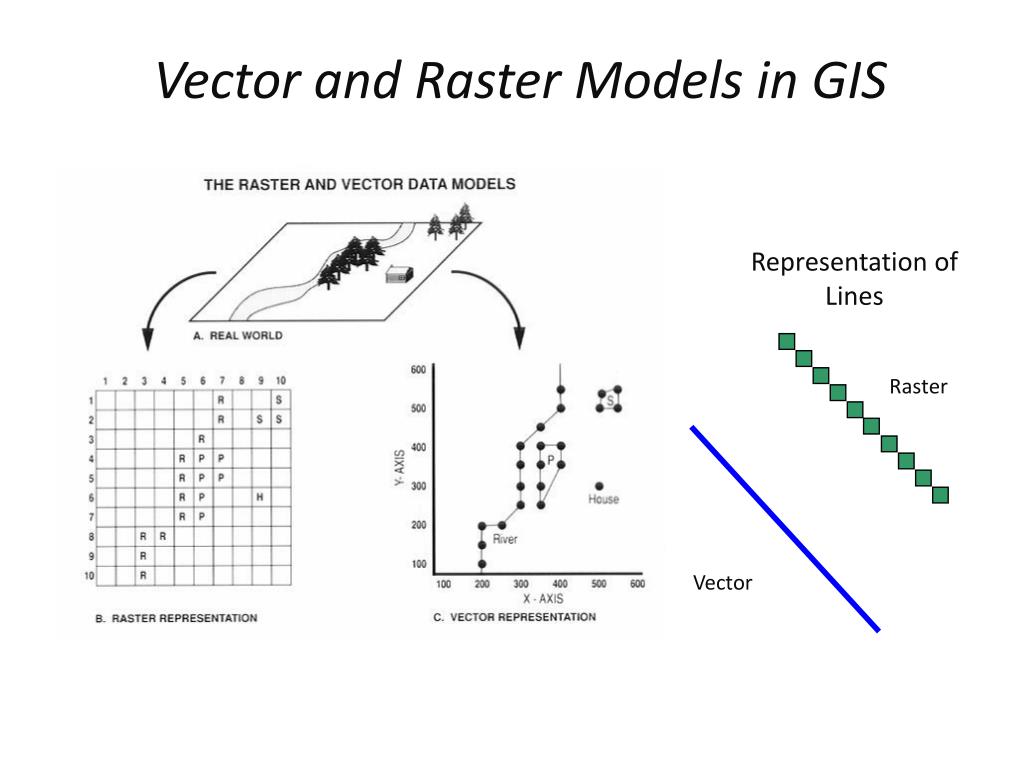
Example- Temperature, air pressure, elevation, flow and distance etc.įigure 1 Vector and Raster data representation Conclusion Example- Administrative borders, roadways, rivers, location of a house, forest area, fallow land etc.Ĥ. While raster data consists of organized cells with specific information, vector data is used for that data with discrete boundaries. It consists of cells organised in rows and columns with each cell having one value.Ĥ. Definition Raster and vector data differ in their definitions, even though they are both types of spatial data. It is used to store data having discrete boundaries in Point, Line and Polygonġ. (see figure 1) Difference Between Vector Data and Raster Data Vector Dataġ. Hence, a number of raster layers are required for the representation of multiple features over a common plane. Pixels represent each and every geographic element. The raster cannot differentiate between objects, everything is simply. Raster data is synonyms with grid data as it consists of pixels with an array of cells. Vector data supports the computation of precise distances between features and can. Examples- Forest area, Agricultural land, snow cover etc.

Polygon feature is mostly distinguished using thematic symbols or colours for visual representation. It takes a minimum of three pairs of coordinates, i.e., X1Y1, X2Y2, X3Y3 to represent an area or polygon. Polygon Data– Polygon data is represented as a closed line encompassing an area.For example rivers, railway lines, roadways etc. The start and endpoints are called nodes and the points on curves are called vertices. Line Data– It is used to represent the data that have linear features which contain at least two pairs of coordinates such as X1 Y1, X2 Y2.For example, the location of a house, location of a well etc. It is most commonly used to represent non-adjacent features and discrete data points. Point Data – is represented by one pair of coordinates ( X and Y) and is considered a dimensionless object because it can neither measure its length nor breadth with its data set. Vector data structure Arc-node model Arcs represent the shape of lines and are split at their intersections with other arcs, where nodes occur nodes represent the beginning and ending vertex of each arc.Maps are often made up of layers of both types of data. As such, vector data tend to define the centres and edges of certain features. There are two main types of spatial data: vector and raster data.

It represents in the form of points, lines and polygons depending upon the feature. Vector data models use X and Y coordinates to define the geographic elements. Based on the nature of the display, this data is classified into two models i.e. Geographic data are geographically referenced data wherein individuals can locate and identify features by a spherical coordinate system i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
